Main Research Fields
-
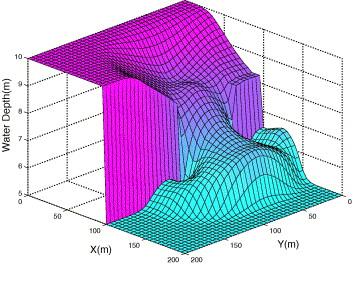
Numerical Solution for Flow Problems using Meshless Methods
This research explores advanced numerical techniques using meshless methods to solve flow problems, focusing on both 1D and 2D shallow water equations. The study incorporates temporal discretization schemes, such as explicit and implicit methods, to ensure stability and accuracy over time. The meshless approach eliminates the need for structured grids, allowing seamless handling of complex geometries and irregular domains. Applications include flood and tsunami modeling, with an emphasis on reducing computational cost while maintaining high accuracy.
-
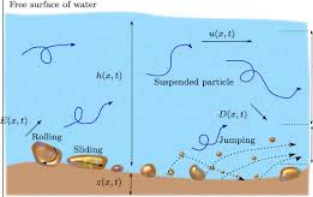
Numerical Solution for Sediment Flow
This research focuses on modeling sediment transport within hydraulic systems by solving the hyperbolic system of equations governing shallow water flows. Sediment transport is incorporated by extending the shallow water equations with additional terms for bedload and suspended load transport. These models address the interaction between fluid flow, sediment transport, and bed morphology, which is crucial for understanding erosion, deposition, and sediment dynamics in natural and engineered waterways. Key aspects of the research include the use of both conservative and non-conservative forms of the governing equations. The conservative form ensures the accurate computation of fluxes across discontinuities like shocks, while the non-conservative form provides flexibility in representing source terms, such as sediment exchange between the bed and flow.
-
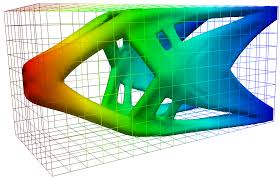
Engineering Optimization
This research focuses on the development of advanced meshless techniques for solving complex partial differential equations (PDEs) in the field of engineering optimization. A primary emphasis is placed on topology optimization, which aims to determine the optimal material distribution within a design domain to achieve maximum performance under given constraints.
The study integrates cutting-edge numerical approaches to address challenges in structural analysis, including shape and material optimization. These methods efficiently solve high-dimensional PDEs while maintaining computational accuracy and robustness. Meshless methods, known for their flexibility in handling irregular geometries and adaptive refinement, are particularly suited for topology optimization problems where the design domain evolves dynamically during the optimization process.
Key applications include lightweight structural design, maximizing stiffness-to-weight ratio, and optimizing components for aerospace, automotive, and civil engineering projects. Temporal and spatial discretization techniques, along with penalty and filter methods, are employed to ensure manufacturability and avoid numerical instabilities like checkerboarding. The integration of engineering optimization with meshless methods opens new opportunities for tackling complex, real-world design challenges.